LeRobot
Visualize LeRobot with Foxglove
To visualize LeRobot with Foxglove, you will work with LeRobot library and Foxglove-SDK to stream real-time data from your robot. This guide will help you set up a live connection to your LeRobot and visualize it in Foxglove.
1. Install LeRobot and Foxglove-SDK
Following the LeRobot installation guide, ensure you have cloned LeRobot repository and created a conda environment:
sudo apt-get install cmake build-essential python-dev pkg-config libavformat-dev libavcodec-dev libavdevice-dev libavutil-dev libswscale-dev libswresample-dev libavfilter-dev pkg-config
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git
cd lerobot
conda create -y -n lerobot python=3.10
conda activate lerobot
conda install ffmpeg -c conda-forge
then, install LeRobot:
pip install -e .
Install the SDK for your robot actuators:
- SO-100
- SO-101
- Koch v1.1
- LeKiwi
pip install -e ".[feetech]"
pip install -e ".[feetech]"
pip install -e ".[dynamixel]"
pip install -e ".[lekiwi]"
You will also need the Foxglove-SDK to stream data to Foxglove (make sure you are in the lerobot conda environment we created above):
pip install foxglove-sdk
2. Use LeRobot API to access robot data
Make sure your hardware is set up and calibrated. When in doubt, follow LeRobot documentation.
Instantiate your robot using the lerobot API and connect to it::
- SO-100
- SO-101
- Koch v1.1
- LeKiwi
from lerobot.common.robots.so100_follower import SO100FollowerConfig, SO100Follower
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.configuration_opencv import OpenCVCameraConfig
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.camera_opencv import OpenCVCamera
from lerobot.common.cameras.configs import ColorMode
RobotConfig = SO100FollowerConfig
Robot = SO100Follower
config = RobotConfig(port="/dev/ttyUSB0", id="foxglove_so100", use_degrees=True)
follower = Robot(config)
follower.connect(calibrate=False)
from lerobot.common.robots.so101_follower import SO101FollowerConfig, SO101Follower
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.configuration_opencv import OpenCVCameraConfig
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.camera_opencv import OpenCVCamera
from lerobot.common.cameras.configs import ColorMode
RobotConfig = SO101FollowerConfig
Robot = SO101Follower
config = RobotConfig(port="/dev/ttyUSB0", id="foxglove_so101", use_degrees=True)
follower = Robot(config)
follower.connect(calibrate=False)
from lerobot.common.robots.koch_follower import KochFollowerConfig, KochFollower
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.configuration_opencv import OpenCVCameraConfig
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.camera_opencv import OpenCVCamera
from lerobot.common.cameras.configs import ColorMode
RobotConfig = KochFollowerConfig
Robot = KochFollower
config = RobotConfig(port="/dev/ttyUSB0", id="foxglove_koch", use_degrees=True)
follower = Robot(config)
follower.connect(calibrate=False)
from lerobot.common.robots.lekiwi import LeKiwiConfig, LeKiwi
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.configuration_opencv import OpenCVCameraConfig
from lerobot.common.cameras.opencv.camera_opencv import OpenCVCamera
from lerobot.common.cameras.configs import ColorMode
RobotConfig = LeKiwiConfig
Robot = LeKiwi
config = RobotConfig(port="/dev/ttyUSB0", id="foxglove_lekiwi", use_degrees=True)
follower = Robot(config)
follower.connect(calibrate=False)
Instantiate a camera to capture the images from your robot, and read robot state:
cam_config = OpenCVCameraConfig(
index_or_path=4,
fps=30,
width=640,
height=480,
color_mode=ColorMode.RGB
)
camera = OpenCVCamera(cam_config)
camera.connect()
obs = follower.get_observation()
print(obs)
frame = camera.async_read(timeout_ms=200)
print(f"Frame shape: {frame.shape}")
Make sure to adjust the following function parameters in the code above:
port- The serial port your robot is connected to. Usepython -m lerobot.find_portto find the correct port.id- The unique identifier for your robot declared when runninglerobot.calibratescript (e.g.,foxglove_so100).index_or_path,fps,width,height,color_mode- Camera parameters established by runninglerobot.find_camerasscript.
3. Use Foxglove-SDK to stream data to Foxglove
Append the following code to your script to use Foxglove-SDK to start a WebSocket server and start streaming data.
import foxglove
from foxglove.schemas import RawImage
import time
from foxglove.channels import RawImageChannel
JOINT_POSITIONS_SCHEMA = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"timestamp": {"type": "number", "description": "Timestamp in seconds"},
"shoulder_pan": {"type": "number", "description": "Shoulder pan joint position in degrees"},
"shoulder_lift": {"type": "number", "description": "Shoulder lift joint position in degrees"},
"elbow_flex": {"type": "number", "description": "Elbow flex joint position in degrees"},
"wrist_flex": {"type": "number", "description": "Wrist flex joint position in degrees"},
"wrist_roll": {"type": "number", "description": "Wrist roll joint position in degrees"},
"gripper": {"type": "number", "description": "Gripper position (0-100)"}
},
"required": ["timestamp", "shoulder_pan", "shoulder_lift", "elbow_flex", "wrist_flex", "wrist_roll", "gripper"]
}
server = foxglove.start_server()
image_channel = RawImageChannel(topic="wrist_image")
pose_channel = foxglove.Channel(
topic="/pose",
schema=JOINT_POSITIONS_SCHEMA,
message_encoding="json"
)
try:
while True:
obs = follower.get_observation()
frame = camera.async_read(timeout_ms=200)
current_pose_msg = {
'timestamp': time.time(),
'shoulder_pan': obs.get("shoulder_pan.pos", 0.0),
'shoulder_lift': obs.get("shoulder_lift.pos", 0.0),
'elbow_flex': obs.get("elbow_flex.pos", 0.0),
'wrist_flex': obs.get("wrist_flex.pos", 0.0),
'wrist_roll': obs.get("wrist_roll.pos", 0.0),
'gripper': obs.get("gripper.pos", 0.0)
}
pose_channel.log(current_pose_msg)
img_msg = RawImage(
data=frame.tobytes(),
width=frame.shape[1],
height=frame.shape[0],
step=frame.shape[1] * 3,
encoding="rgb8",
)
image_channel.log(img_msg)
time.sleep(0.03)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Stopping server...")
finally:
server.stop()
camera.disconnect()
follower.bus.disconnect()
Run your LeRobot visualization script:
python your_lerobot_foxglove_script.py
4. Visualize in Foxglove
Make sure you are on the same network as your robot. In Foxglove, select Open connection from the dashboard or left-hand menu.
Select Foxglove WebSocket in the Open a new connection dialog, then enter the URL of the server:
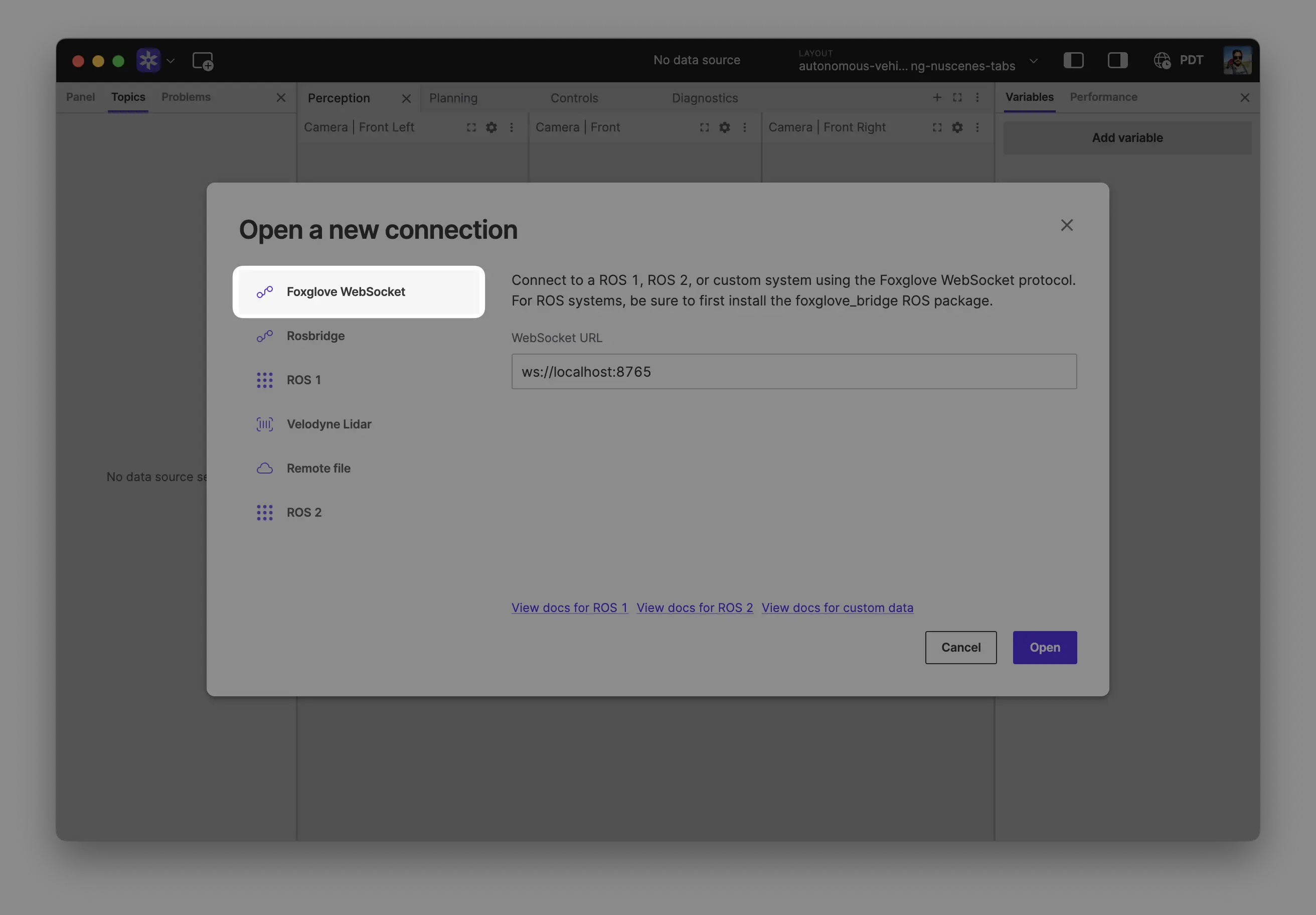
Click "Open" to connect.
Local development: Use ws://localhost:8765 when running the server on the same machine as Foxglove.
Robot connection: Use ws://ROBOT_IP:8765 when connecting to a server running on your robot, where ROBOT_IP is your robot's IP address on the network.
You can now add an image panel to visualize the camera feed, and use the plot panel to plot joint positions.
The LeRobot + Foxglove tutorial provides a complete working example, including viewing the robot's 3D model.
Learn more
- Explore the complete LeRobot + Foxglove integration example
- Check out LeRobot's documentation for robot setup and configuration
- Learn about URDF visualization in Foxglove's 3D panel
- Use layouts to save and share your LeRobot visualization setups
- Store and share your robotics data using the data platform