Getting Started with SO-100 Robot Arm
SO-100 is a 3D-printed 6-DOF robot arm developed by the Robot Studio and Hugging Face. The easiest way to visualize the arm with Foxglove is to use LeRobot and an example script featured as an example in the Foxglove SDK repository.
Step 1: Software Installation
Install LeRobot
First, set up the LeRobot environment:
# Install system dependencies (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo apt-get install cmake build-essential python-dev pkg-config \
libavformat-dev libavcodec-dev libavdevice-dev libavutil-dev \
libswscale-dev libswresample-dev libavfilter-dev
# Clone LeRobot repository
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git
cd lerobot
# Create conda environment
conda create -y -n lerobot python=3.10
conda activate lerobot
conda install ffmpeg -c conda-forge
# Install LeRobot with SO-100 support
pip install -e ".[feetech]"
Install Foxglove SO-100 Visualization Dependencies
# Make sure you're in the lerobot environment
conda activate lerobot
# Clone the Foxglove SDK
git clone https://github.com/foxglove/foxglove-sdk
cd foxglove-sdk/python/foxglove-sdk-examples/so100-visualization
# Install additional dependencies for this example
pip install -r requirements.txt
Step 2: Run Your First Visualization
Basic Robot Visualization
Make sure you completed your hardware setup following LeRobot's SO-100 guide and have your robot connected.
Navigate to the Foxglove SDK So-100 example directory:
conda activate lerobot # Ensure you're still in the lerobot environment
cd foxglove-sdk/python/foxglove-sdk-examples/so100-visualization
Start with the simplest example - just the robot without cameras:
python main.py \
--robot.port=/dev/ttyUSB0 \
--robot.id=my_so100_arm
Replace /dev/ttyUSB0 with your actual robot port and my_so100_arm with the ID you used during calibration.
Connect to Foxglove
In Foxglove, select Open connection from the dashboard or left-hand menu.
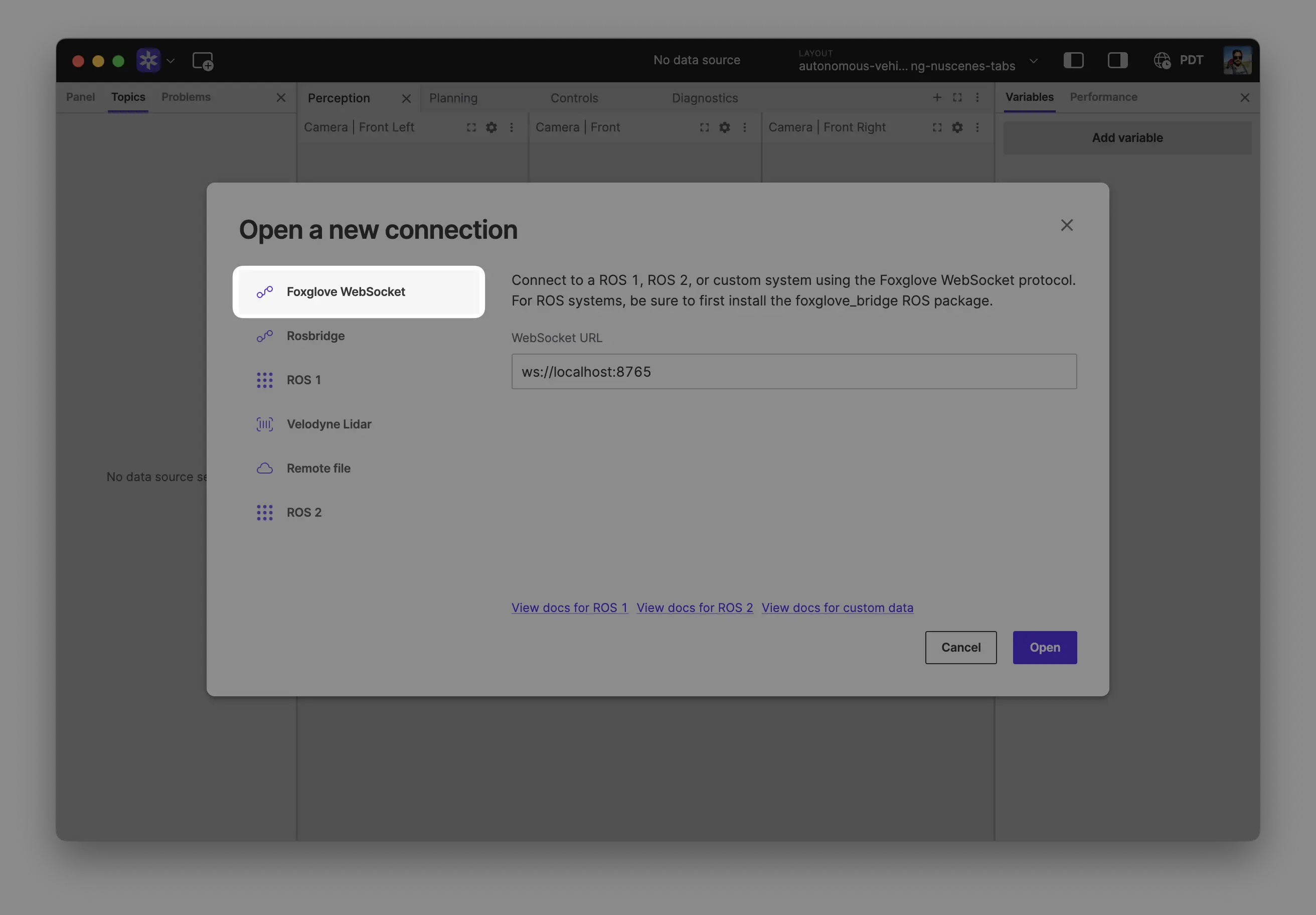
Select Foxglove WebSocket in the Open a new connection dialog, then enter the URL of your SDK server (ws://localhost:8765 by default):
Open the layout included with the example. In the layout dropdown in the application toolbar, select Import from file..., and select foxglove-sdk/python/foxglove-sdk-examples/so100-visualization/foxglove/lerobot_layout.json.
You should now see your robot's data streaming live!
Step 3: Advanced Visualizations
Add Camera Feeds
Include wrist and environment cameras:
python main.py \
--robot.port=/dev/ttyUSB0 \
--robot.id=my_so100_arm \
--robot.wrist_cam_id=0 \
--robot.env_cam_id=4
Run lerobot's python -m lerobot.find_cameras opencv to find available camera IDs and resolutions.
In the main.py, we've made some assumptions on the camera resolution and FPS. If you get errors related to that, you might need to adjust the values in the script.
Record Data to MCAP
Capture your robot session for later analysis:
python main.py \
--robot.port=/dev/ttyUSB0 \
--robot.id=my_so100_arm \
--robot.wrist_cam_id=0 \
--robot.env_cam_id=4 \
--output.write_mcap \
--output.mcap_path=my_robot_session.mcap
Learn More
- LeRobot Documentation - Complete robot setup guide
- Foxglove SDK Documentation - SDK reference and examples
- Data Playback - Analyze recorded robot sessions